Why Base 60?
The sexagesimal system invented by the Babylonian brings us a very different perspective on our current place value system. At first glance, it is a bit inconvenient and challenging for us to use 60 and its powers for representing numbers or doing calculations. Some people like me might prefer solving sexagesimal problems by firstly converting them into base 10 numbers before doing calculations. However, we cannot deny the fact that the number 60 is to some extent more attractive and useful as the base for a number notational system. For instance, 60 is divisible by 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, 30 and 60, whereas 10 is only divisible by 1, 2, 5 and 10. Most importantly, the prime number 3 is one of the divisors of 60 whilst all the multiples of 10 can not be divided by 3. Having a variety of divisors made calculation more convenient in the past, especially for merchants who attempted to divide up a huge amount of goods [1].
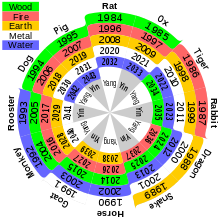
It is interesting that the sexagesimal system still exists in our daily lives. Our international time-telling system is a good example of the application of sexagesimal. Every 60 seconds is equivalent to one minute; every 60 minutes can be represented by one hour. The Chinese zodiac and time-telling system is another example showing the contemporary usage of sexagesimal. In the Chineses calendar, the combination of 5 elements and 12 animals constitutes a 60-year cycle which can be illustrated by the following diagram [2]. Besides, sexagesimal can also be used to describe angles as we divide a circle into 360 degrees.
After doing further research on it, I found that babylonian sexagesimal system was developed based on Sumerians’ numeric system [3]. The invention of babylonian mathematics was a result of multicultural integration from two earlier groups whose number systems were based on 5 and 12 respectively [3]. It is an amazing journey for us to study the history of babylonian sexagesimal system and realize the importance of cultural diversity. [1] Neugebauer, O. (1969), "The Exact Sciences In Antiquity", Acta Historica Scientiarum Naturalium et Medicinalium, Dover, 9: 17–19, ISBN 0-486-22332-9, PMID 14884919 [2] Wikipedia, Sexagesimal - Wikipedia [3] Gill, N.S. "Babylonian Mathematics and the Base 60 System." ThoughtCo, Aug. 27, 2020, thoughtco.com/why-we-still-use-babylonian-mathematics-116679.

What an interesting point about a major difference between base 10 and base 60 systems being the inclusion of the prime number 3. Also, thank you for including the Chinese zodiac image.
ReplyDelete